Pregnancy ICD 10
The Pregnancy ICD 10 code belong to the Chapter 15 – Pregnancy, Childbirth, and the Puerperium of the ICD-10-CM and these codes take sequencing priority over all the other chapter codes.
The pregnancy ICD 10 codes range from O00- O9A.
Coding for Pregnancy is sometimes difficult as there are multiple factors that need to be taken into consideration like the trimester, fetus identification, whether it is a high risk pregnancy or a normal pregnancy and other additional code like the code for the weeks of gestation from chapter 22.
A clear documentation with all the above necessary information and an understanding of the coding guidelines will make the coding much easier and accurate.
General rules to be followed while coding pregnancy ICD 10 visits-
- The chapter 15- Pregnancy, Childbirth, and the Puerperium codes can be used only to code the maternal records and never the newborn records.
- Any complications or conditions arising due to pregnancy, childbirth or puerperium should be coded using the codes from this chapter.
- As mentioned earlier the chapter 15 codes take sequencing priority over all other chapter codes.
- If the provider has documented that the pregnancy is incidental to the visit, which means that the reason for the visit was not pregnancy related and the provider did not care for the pregnancy, the code to be used is Z33.1, Pregnant state, incidental and not the chapter 15 codes.
- The last digit of most of the chapter 15 codes indicates the trimester of pregnancy and its counted from the first day of the last menstrual period.

- Provider’s documentation of the trimester or the number of weeks of pregnancy for the current visit/admission should be the basis of the selection of the final character for the trimester.
- The concept of trimester as the final character is not applicable if the condition always occurs in a specific trimester and not all trimesters.
- Few codes have final characters only for certain trimesters because these conditions are unique to those trimesters.
- If a patient is admitted to the hospital due to pregnancy complications during one trimester and is discharged when she is in the subsequent trimester, the trimester during which the complication developed or when the patient was admitted should be considered while coding. The same rule applies to any pre-existing condition also.
- The “unspecified trimester” code should be used only if there is insufficient documentation regarding the trimester and this code should be rarely used.
- Certain code categories require 7th characters to identify the fetus. The following are the 7th characters-
- 0 –single gestation, insufficient documentation regarding the fetus affected
- 1- fetus 1
- 2- fetus 2
- 3- fetus 3
- 4- fetus 4
- 5- fetus 5
- 9- other fetus
- Coding encounters for normal versus high risk pregnancies-
- Encounter for a routine visit in case of a normal pregnancy is coded with the Z34 category code from chapter 22 code and this should not be used with the chapter 15 codes.
- Supervision of high-risk pregnancy is coded with codes from the category O09.
- If the high-risk pregnancy complicates the labor and delivery, the appropriate chapter 15 code is coded.
- A labor and delivery without any complications is coded as O80, Encounter for full-term uncomplicated delivery.
- When no delivery happens during the visit, the code for the pregnancy complication which lead to the visit is coded as the principal diagnosis.
- When multiple complications are treated or monitored during a visit, the codes for the complications can be sequenced in any order.
- Coding encounters when delivery occurs-
- The outcome of delivery code Z37 should be coded on every maternal record in the event of a delivery.
- When a pregnant patient is admitted with a pregnancy complication and delivers during that admission, the reason for the admission is coded as the principal diagnosis.
- If there were multiple complications, the complication most related to the admission needs to be sequenced first. Any delivery complications are coded as secondary diagnoses codes.
- If the patient is admitted with a pregnancy complication which necessitated a Cesarean delivery, the code for the complication should be sequenced first. But if the reason for admission was different from the reason for the C-section, the reason for the admission will be sequenced first.
- The chapter 15 has few categories for pre-existing conditions and conditions arising during pregnancy. Therefore, it is important to determine if a condition was pre-existing or originated during pregnancy.
Pregnancy ICD10 CM codes from Chapter 15
Chapter 15 codes are very extensive. The categories, their descriptions and some of the conditions included under the codes have been given below-
The Code Categories

Categories – ICD 10 Code for pregnancy with abortive outcome (O00- O08)

- Ectopic pregnancy (Code range- O00.00 – O00.91)– This is a potentially life-threatening condition in which the fertilize egg is implanted outside the uterus, usually in one of the fallopian tubes or occasionally in the abdomen or ovaries.
- Hydatidiform mole (Code range- O01.0 – O01.9) – Also known as molar pregnancy is an abnormal fertilized egg or a non-cancerous tumor of the placental tissue which mimics a normal pregnancy initially but later leads to vaginal bleeding along with severe nausea and vomiting.
- Other abnormal products of conception (Code range- O02.0 – O02.9)
- Blighted ovum (O02.0)- A condition where the fertilized egg implants in the uterus but does not develop into an embryo.
- Missed abortion (O02.1)- The retention of a non-viable fetus along with the placenta and embryonic tissues inside the uterus without the body recognizing the loss of pregnancy and therefore failing to naturally expel the non-viable contents like in spontaneous abortion.
- Spontaneous abortion (Includes Miscarriage) (Code range- O03.0 – O03.9)– Miscarriage before 20 weeks of gestation resulting from the improper development of the fetus.
- Complications following (induced) termination of pregnancy (Code range- O04.5 – O04.89) – This includes the complications followed by abortions that are induced intentionally.
- Failed attempted termination of pregnancy (Code range- O07.0 – O07.4) –This includes failure of attempted induction of termination of pregnancy and incomplete elective abortion.
- Complications following ectopic and molar pregnancy (Code range- O08.0 – O08.9)- This category codes are for use with the categories O00- O02, for any associated complications.
Supervision of high-risk pregnancy (ICD 10 Code range- O09.0- O09.93)
A pregnancy is considered high-risk if the woman is-
- 17 years or younger
- 35 years or older
- Underweight or Overweight or Obese
- Pregnant using assisted reproductive technology
- Pregnant with twins, triplets, or other multiples
- Hypertensive, has diabetes, depression, HIV positive or other pre-existing health problems
- Having a history of infertility, ectopic or molar pregnancies.
- Having a history of prior complicated pregnancy or pregnancies resulting in a pre-term delivery or a child with a genetic problem.
- Having a history of an in-utero procedure during previous pregnancy.
- Having social problems that is a threat to pregnancy.
A high-risk pregnancy is a threat to the health and the life of the mother and the fetus.
Code categories for coding edema, proteinuria and hypertensive disorders in pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium (Code range- O10-O16)

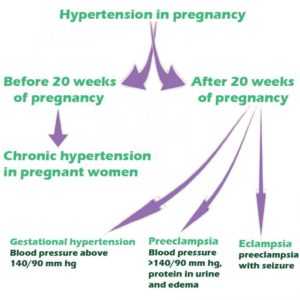
- Pre-existing hypertension complicating pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium (Code range- O10.011-O10.93) – A pregnancy complication arising due to the patient being hypertensive, having proteinuria (increased levels of protein in urine), hypertensive heart disease, hypertensive CKD or both prior to the pregnancy.
- Pre-existing hypertension with pre-eclampsia (Code range- O11.1-O11.9)- Chronic/ pre-existing hypertension in a pregnant patient with signs of pre-eclampsia (High blood pressure that begins usually after 20 weeks of gestation.)
- Gestational [pregnancy-induced] edema and proteinuria without hypertension (Code range- O12.00-O12.25)- A condition arising during pregnancy usually after 20 weeks of gestation and which resolves by 12 weeks postpartum.
- Gestational [pregnancy-induced] hypertension without significant proteinuria (Code range- O13.1-O13.9)- High blood pressure (≥140/90) during the latter part of pregnancy (after 20 weeks of gestation) without the presence of protein in urine.
- Pre-eclampsia (Code range- O14.00-O14.95)- This is a combination of gestational hypertension and proteinuria during or after 20 weeks of pregnancy. This is a potentially dangerous complication and poses threat to the mother and the baby.
- HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelet count) syndrome– (Code range O14.20- O14.25) – A very rare condition seen in pregnant patients mostly with pre-eclampsia usually before the 37th week of pregnancy.
- Eclampsia (Code range- O15.00-O15.9) – Serious complication of pre-eclampsia leading to seizures during pregnancy.
- Unspecified maternal hypertension (Code range- O16.1-O16.9).

- Hemorrhage in early pregnancy (Code range- O20.0-O20.9)- Includes hemorrhage before completion of 20 weeks of gestation.
- Threatened abortion (O2.0)- Vaginal bleeding before completion of 20 weeks of pregnancy indicating a possible miscarriage.
- Excessive vomiting in pregnancy (Hyperemesis gravidarum) (Code range- O21.0-O21.9)- Severe, persistent nausea and vomiting during pregnancy leading to dehydration, weight loss and electrolyte imbalance.
- Venous complications and hemorrhoids in pregnancy (Code range- O22.00-O22.93)- Includes varicose veins, genital varices, superficial thrombophlebitis, phlebothrombosis, hemorrhoids and cerebral venous thrombosis.
- Infections of genitourinary tract in pregnancy– (Code range- O23.00-O23.93)- These codes should be accompanied with additional codes to identify the organism causing the infection.
- Diabetes mellitus in pregnancy, childbirth, and the puerperium– (Code range- O24.011-O24.93)
- Pre-existing Diabetes mellitus (type 1 and type 2) (Code range- O24.011-O24.33)
- Gestational Diabetes mellitus (Code range- O24.410-O24.93)
- Malnutrition in pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium (Code range- O25.10-O25.3)
- Maternal care for other conditions predominantly related to pregnancy (Code range- O26.00-O26.93).
The conditions under this category range include-
-
- Excessive weight gain in pregnancy
- Low weight gain in pregnancy
- Pregnancy care for patient with recurrent pregnancy loss
- Retained intrauterine contraceptive device in pregnancy
- Herpes gestations– An itchy skin eruption that usually happens in the second or third trimester of pregnancy.
- Maternal hypotension syndrome
- Liver and biliary tract disorders in pregnancy, childbirth and puerperium
- Subluxation of symphysis (pubis) in pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium
- Pregnancy related exhaustion and fatigue
- Pregnancy related peripheral neuritis
- Pregnancy related renal disease
- Uterine size-date discrepancy complicating pregnancy
- Spotting complicating pregnancy
- Pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy (PUPPP) – chronic hives-like rash seen during pregnancy causing severe pruritus.
- Cervical shortening – Shortening of the length of the uterine cervix which increases the risk of preterm labor.
- Abnormal findings on antenatal screening of mother (Code range- O28.0-O28.9) – Includes abnormal hematological, biochemical, cytological, ultrasonic, radiological, chromosomal and genetic findings.
- Complications of anesthesia during pregnancy (Code range- O29.011-O29.93) – includes complications arising from the administration of general, regional or local anesthetic, analgesic or other sedation during pregnancy. The complications include-
- Aspiration pneumonitis
- Pressure collapse of lung
- Cardiac arrest
- Cardiac failure
- Cerebral anoxia
- Toxic reaction to local anesthesia
- Spinal and epidural anesthesia induced headache
- Failed or difficult intubation

- Multiple gestation (Code range O30.001- O30.93) – A gestation with more than one fertilized egg implanted in the uterus.
This includes twin pregnancies (including conjoined, monochorionic/diamniotic, dichorionic/diamniotic), triplet pregnancies (including two or more monochorionic/ monoamniotic fetus, trichorionic/triamniotic pregnancy), quadruplet pregnancy (including two or more monochorionic/ monoamniotic fetus, trichorionic/triamniotic pregnancy).
Additional codes for the complications need to be coded.
- Complications specific to multiple gestation (Code range O31.00X0- O31.8X99)
- Papyraceous fetus– A rare complication of multiple gestations in which one fetus dies and gets compressed or flattened between the living fetus and the uterine wall usually in the second trimester. This parchment like remains of the dead fetus is retained in-utero
- Maternal care for malpresentation of fetus (Code range O32.0XX0- O32.9XX9)
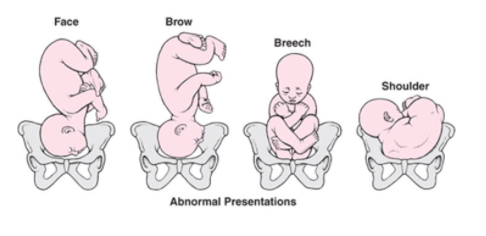
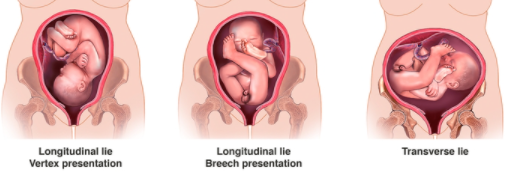
Unstable lie- When the fetal lie and presentation repeatedly varies between longitudinal, transverse and oblique presentations.
Compound presentation- When an arm or sometimes a foot, lies alongside the presenting part which is the head.
- Maternal care for disproportion (Code range O33.0 O33.9)- The following listed conditions leading to disproportion warrants observation, hospitalization or other obstetric care of the mother, or for cesarean delivery before onset of labor-
- Deformity of maternal pelvic bones
- Generally contracted pelvis
- Inlet contraction of pelvis
- Outlet contraction of pelvis
- Mixed maternal and fetal origin
- Unusually large fetus
- Hydrocephalic fetus
- Maternal care for abnormality of pelvic organs (Code range O34.00- O34.93)- The following listed abnormality of pelvic organs requires observation, hospitalization or other obstetric care of the mother, or for cesarean delivery before onset of labor-
- Congenital malformation of uterus
- Benign tumor of corpus uteri
- Uterine scar from previous surgery
- Cervical incompetence
- Incarceration, prolapse or retroversion of gravid uterus
- Abnormality of vagina
- Abnormality of vulva and perineum
- Maternal care for known or suspected fetal abnormality and damage (Code range O35.0XX0- O35.9XX9)- Conditions included are suspected-
- Central nervous system malformation in fetus
- Chromosomal abnormality in fetus
- Hereditary disease in fetus
- Damage to fetus from viral disease in mother
- Damage to fetus from alcohol
- Damage to fetus by drugs
- Damage to fetus by radiation
- Maternal care for other fetal problems (Code range O36.0110- O36.93X9)- Conditions included are-
- Rhesus isoimmunization
- Anti-A sensitization
- Other isoimmunization
- Hydrops fetalis (large amounts of fluid accumulation baby’s tissues and organs)
- Intrauterine death
- Suspected poor fetal growth
- Suspected placental insufficiency
- Excessive fetal growth
- Viable fetus in abdominal pregnancy
- Inconclusive fetal viability
- Decreased fetal movements
- Fetal anemia and thrombocytopenia
- Abnormalities of the fetal heart rate or rhythm
- Polyhydramnios (hydramnios) (Code range O40.1XX0- O40.9XX9)- An excess amount of amniotic fluid in the amniotic sac than the accepted normal values.
- Other disorders of amniotic fluid and membranes (Code range O41.00X0- O41.93X9) –
- Oligohydramnios – volume of amniotic fluid is less than expected for gestational age.
- Infection of amniotic sac and membranes
- Chorioamnionitis – inflammation/ infection (usually bacterial) of the fetal membranes (amnion and chorion).
- Placentitis – inflammation/infection of the placenta
- Premature rupture of membranes (Code range O42.00- O42.92)-
- Placental disorders (Code range O43.011- O43.93)- Deviation from the normal placental structure.
- Placental transfusion syndromes
- Fetus-to-fetus placental transfusion syndrome
- Malformation of placenta
- Circumvallate placenta
- Velamentous insertion of umbilical cord
- Morbidly adherent placenta (Placenta accrete, Placenta increta, Placenta percreta)
- Placental infarction
- Placenta previa (Code range O44.00- O44.53)- Condition in which the placenta is implanted in the lower parts of the uterus
- Premature separation of placenta [abruptio placentae] (Code range O45.001- O45.93)
- Antepartum hemorrhage, not elsewhere classified (Code range O46.001- O46.93)
- False labor (includes Braxton Hicks contractions, threatened labor) (Code range O47.00- O47.9) – an irregular tightening sensation felt by the pregnant mother after the 28th week of pregnancy.
- Late pregnancy (Code range O48.0- O48.1)
- Post-term pregnancy (O48.0)
- Prolonged pregnancy (O48.1)
| Pregnancy ICD 10 – Example 1 A 30-year-old woman is admitted with severe pre-eclampsia in the 25th week of pregnancy. Code the appropriate ICD-10-CM diagnosis codes.
(Ans: O14.12, Z3A.25) |
| Pregnancy ICD 10 – Example 2 A 28-year-old type 1 diabetic woman returns for followup to her obstetrician’s office after delivering her child last week. She will be monitored by her obstetrician closely for a few weeks. Code the appropriate ICD-10-CM diagnosis codes for the visit.
(Ans: O24.03, E10.9) |
Complications of Labor and Delivery (Code range O60-O77)

- Preterm labor (with or without delivery) (Code range O60.00- O60.23X9) – spontaneous onset of labor before 37 completed weeks of gestation.
- Failed induction of labor (Code range O61.0- O61.9)
- Abnormalities of forces of labor (Code range O62.0- O62.9)
- Primary inadequate contractions
- Secondary uterine inertia
- Other uterine inertia
- Precipitate labor
- Hypertonic, incoordinate, and prolonged uterine contractions
- Long labor (Code range O63.0- O63.9)
- Obstructed labor due to malposition and malpresentation of fetus (Code range O64.0XX0- O64.9XX9) – Condition arising due to any one of the following-
- Incomplete rotation of the fetal head
- Breech presentation
- Face presentation
- Brow presentation
- Shoulder presentation
- Compound presentation
- Obstructed labor due to maternal pelvic abnormality (Code range O65.0- O65.9)- Condition arising due to any one of the following-
- Deformed pelvis
- Generally contracted pelvis
- Pelvic inlet contraction
- Pelvic outlet and mid-cavity contraction
- Fetopelvic disproportion
- Abnormality of maternal pelvic organs
- Other obstructed labor (Code range O66.0- O66.9)- Condition arising due to any one of the following-
- Shoulder dystocia (when baby’s anterior shoulder gets trapped above mother’s pubic bone while vaginal delivery)
- Locked twins
- Unusually large fetus
- Failed trial of labor
- Failed attempted vaginal birth after previous cesarean delivery
- Attempted application of vacuum extractor and forceps
- Multiple fetuses
- Labor and delivery complicated by intrapartum hemorrhage, not elsewhere classified (Code range O67.0- O67.9)
- Labor and delivery complicated by abnormality of fetal acid-base balance (Code O68)
- Labor and delivery complicated by umbilical cord complications (Code range O69.0XX0- O69.9XX9)- Condition arising due to any one of the following
- Prolapse of cord
- Cord around neck, with or without compression
- Cord entanglement, with or without compression
- Short cord
- Vasa previa
- Vascular lesion of cord
- Perineal laceration during delivery (Code range O70.0- O70.9)- Includes episiotomy extended by laceration and anal sphincter tear.
- Other obstetric trauma (Code range O71.00- O71.9)- Includes obstetrics injury from instruments. Conditions include-
- Rupture of uterus
- Postpartum inversion of uterus
- Laceration of cervix
- High vaginal laceration
- Damage to pelvic joints and ligaments
- Hematoma of pelvis
- Trauma to perineum and vulva
- Postpartum hemorrhage (immediate or delayed) (Code range O72.0- O72.3)
- Retained placenta and membranes, without hemorrhage (Code range O73.0- O73.1)
- Complications of anesthesia during labor and delivery (Code range O74.0- O74.9). The complications include-
- Aspiration pneumonitis
- Cardiac complications
- Central nervous system complications
- Toxic reaction to local anesthesia
- Spinal and epidural anesthesia-induced headache
- Failed or difficult intubation for anesthesia
- Other complications of labor and delivery, not elsewhere classified (Code range O75.0- O75.9). – The complications include-
- Maternal distress or shock during labor and delivery
- Pyrexia
- Infection
- Delayed delivery after induced rupture of membranes
- Maternal exhaustion
- Spontaneous onset of labor after 37 weeks of gestation but before 39 weeks, with delivery by planned C-section.
- Abnormality in fetal heart rate and rhythm complicating labor and delivery (Code O76). Includes
- Depressed fetal heart rate tones
- Fetal bradycardia
- Fetal heart rate decelerations
- Fetal heart rate irregularity
- Fetal heart rate abnormal variability
- Fetal tachycardia
- Non-reassuring fetal heart rate or rhythm
- Other fetal stress complicating labor and delivery (Code range O77.0- O77.9). Complications include-
- Meconium in amniotic fluid
- Fetal stress due to drug administration
Encounter for delivery (Code range- O80-O82)
Complications predominantly related to the puerperium (Code range O85-O92)

- Puerperal sepsis (O85). Includes-
-
- Postpartum sepsis
- Puerperal peritonitis
- Puerperal pyemia
- Other puerperal infections (Code range O86.00- O86.89). Includes-
- Infection of obstetric surgical wound
- Sepsis following an obstetrical procedure
- Cervicitis, endometritis or vaginitis following delivery
- Urinary tract infections
- Pyrexia of unknown origin
- Puerperal septic thrombophlebitis
Note: An additional code for the organisms causing the infection needs to be coded.
- Venous complications and hemorrhoids in the puerperium (Code range O87.0- O87.9)
- Superficial thrombophlebitis
- Deep phlebothrombosis
- Hemorrhoids
- Cerebral venous thrombosis
- Varicose veins of lower extremity
- Obstetric embolism (Code range O88.011- O88.83). Includes-
- Air embolism
- Amniotic fluid embolism
- Thromboembolism
- Obstetric pyemic and septic embolism
- Complications of anesthesia during the puerperium (Code range O89.01- O89.9). Includes-
- Aspiration pneumonitis
- Cardiac complications
- Central nervous system complications
- Toxic reaction to local anesthesia
- Spinal and epidural anesthesia-induced headache
- Failed or difficult intubation for anesthesia
![]()
-
- Disruption of cesarean delivery wound
- Disruption of perineal obstetric wound
- Hematoma of obstetric wound
- Peripartum cardiomyopathy
- Postpartum acute kidney failure
- Postpartum thyroiditis
- Postpartum mood disturbance
- Anemia of the puerperium

-
- Infection of nipple
- Abscess of breast
- Nonpurulent mastitis
- Other disorders of breast and disorders of lactation associated with pregnancy and the puerperium (Code range O92.011- O92.79). Includes-
- Retracted nipple
- Cracked nipple
- Agalactia
- Hypogalactia
- Suppressed lactation
- Galactorrhea
-
Other obstetric conditions, not elsewhere classified (Code range O94-O9A)

- Sequelae (Late effects) of complication of pregnancy, childbirth, and the puerperium (O94)- Includes conditions or late effects that may occur any time after the puerperium.
- Maternal infectious and parasitic diseases classifiable elsewhere but complicating pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium (Code range O98.011-O98.93). Includes-
- Tuberculosis
- Syphilis
- Gonorrhea
- Viral hepatitis
- Protozoal diseases
- HIV disease
- Other infectious diseases
Note: Codes from chapter 1 should be coded to identify specific infectious and parasitic diseases.

Some of the conditions included are-
- Anemia
- Obesity
- Abnormal glucose
- Use of alcohol, drugs and tobacco
- Other diseases related to blood, endocrine, and other body systems.
- Other mental disorders
- Streptococcus B carrier state
- Bariatric surgery status

-
- Malignant neoplasms
- Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes
- Physical, psychological and sexual abuse
| Pregnancy ICD 10 – Example 3 A 42-year-old pregnant woman in her 30th week of pregnancy comes to the clinic with complaints of decreased fetal movements. The ultrasound examination revealed bradycardia in fetus. Code the appropriate ICD-10-CM diagnosis codes.
(Ans: O09.523, O76, Z3A.30) |
| Pregnancy ICD 10 – Example 4Sarah, a 30-year-old woman with AIDS in her 28th week of pregnancy is admitted to the observation unit with acute kidney failure. Assign the ICD-10-CM diagnosis codes for the scenario.
(Ans: O98.713, B20, N17.9, Z3A.28) |
