Asthma ICD 10
In this topic Let us learn What is Asthma, Types, Asthma ICD 10 guidelines and codes along with some examples.
We are all very familiar with the term “Asthma” as many of us are either suffering from this or known people to us are affected with asthma. Everybody knows it is a respiratory disease which causes breathing problems. In this topic we are trying to add more knowledge to this.
Asthma is a chronic disease, means it does not have a complete cure. Hence people with asthma should learn to live with it. Though it cannot be cured completely, symptoms can be reduced if we give proper care and treat on time.
When talking about coding asthma, we need to discuss on the symptoms of asthma and changes of airway during asthma attack and most importantly the codes and guidelines.
Asthma causes symptoms like shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing or chest tightness. Severity differs in each person. For some people it may be mild but some others suffer on a daily basis with asthma and become a life threatening condition for them.
What happens to our Lungs(Center of respiratory system)during asthma attack:
During asthma attack, muscles around the airway gets tighten and the lining inside the airways becomes swollen and produce extra mucus. This makes airway to become narrow and partially block airflow in and out of air sacs.
Below picture gives a clear understanding of the position of lungs (A), normal airway (B) and airway during asthma attack (C).
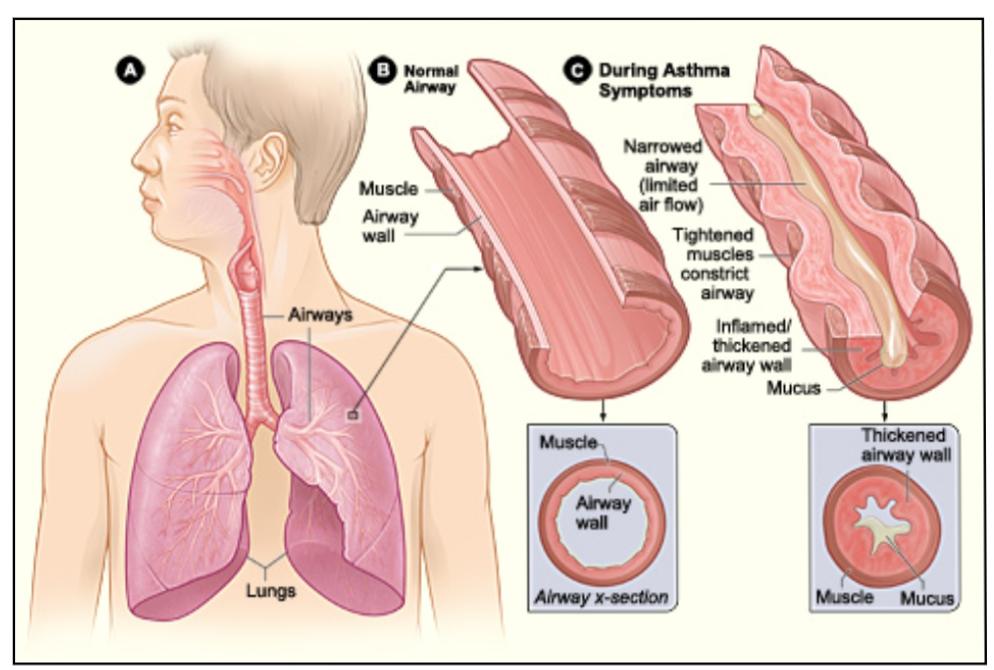
Apart from knowing the symptoms and doing a lung physical examination the physician will also do few test measures like X-ray, spirometry, allergy testing, nitric oxide breath test or peak flow to determine the type of asthma and it’s severity. Hence a coder should definitely pay attention to these areas as well.
Common terms found in medical record related to asthma:
Asthma exacerbation: – It is nothing but an acute increase of symptoms in a person with asthma. This can be coded only with the Physician diagnosis.
Status asthmatics : – Another term for this is severe asthma exacerbation. It is considered as severe as this may lead to even respiratory failure due to hypoxemia. As soon as a patient comes to emergency room with asthma symptoms, physician treats initially with medicines such as bronchodilators. If patient has status asthmatics they do not respond to these medicines.
Inhaler : – Medicine filled inhalers are given to patient to use comfortably at any place when symptoms occurs suddenly.
Nebulizer : – Electricity powered machine filled with liquid medication which turns to mist and the patient breath in.
Nasal spray : – A bottle with liquid medicine made with the ease of spraying to nose.
PFT : – Pulmonary Function Test, use to check the lung function by measuring lung volume, capacity, rates of flow and gas exchange.
Medications for asthma:
When reviewing a medical record for an asthma patient we get to see different types of medications either given in the clinic or prescribed. Few examples are given below.
Long term asthma controlled medications like inhaled corticosteroids (fluticasone, mometasone)
Quick relief medications like Albuterol, Atrovent
Allergy shots for allergic asthma
Classification
Below are few types of asthma which we frequently come across in the medical record.
| Types of Asthma | Description |
|---|---|
| Allergic Extrinsic | Very common form of asthma which occurs when the person gets exposed to any allergens like pollen, mites. |
| Intrinsic non-allergic | This is not allergic; instead it gets triggered by weather conditions, exercise, infections or stress. |
| Childhood | Children at any age can diagnose with asthma. They are more sensitive to allergens, so chances of getting asthma are high. |
| Their symptoms may completely disappear after few years. Experts say this may be due to the growth of airways along with body growth. | |
| Cough variant | It is so called because of the main symptom, dry cough. |
| Mild intermittent | As the name says symptoms occur intermittently, twice in a week or month. It does not give much trouble to the patient. |
| Mild persistent | This type of asthma occurs more than 2 times in a week with regular breathing difficulties to an extent of disturbing daily activities. |
| Moderate persistent | These patients suffer from symptoms daily and last for several days. |
| Severe persistent | Unlike all other types of asthma, this has got severe continuous symptoms every day. It requires immediate treatment to improve the lung function. |
| Exercise induced | Patient starts getting symptoms during or after exercise. |
ICD-10 guidelines and Codes:
Refer Chapter 10 (Diseases of the respiratory system (J00- J99) in ICD-10-CM for Asthma guidelines.
ICD codes are arranged in alphabetical order. One should clearly understand the type of asthma and code to the highest specificity. Most types of Asthma fall into category J45.
For example, if asthma unspecified and asthma exacerbation is mentioned in the final impression, code should be assigned for asthma exacerbation only.



Combination codes:
Here is the tricky part comes in coding asthma. At times we do not need to code asthma, instead assign another more specified respiratory condition or in other words use a combination code with another condition.
| Conditions in medical record | ICD to assign | Guideline |
|---|---|---|
| Asthma, COPD | J44.9 | Code only COPD as it is more specified |
| Asthma exacerbation, COPD | J44.9, J45.901 | Asthma with additional specificity or any type can be coded along with COPD |
| Moderate persistent asthma, COPD | J44.9, J45.40 | Asthma with additional specificity or any type can be coded along with COPD |
Asthma ICD 10 Example 1:
Peter, 69 year old male comes to clinic with shortness of breath from past few days. He had travelled to Austin last week to meet his grand children. He does not have a history of COPD in the past, but has history of asthma. He states he does not use inhaler. He is a non-smoker.
Physician examined the patient and ordered spirometry test. Along with the test results he mentioned in final impression as “allergic extrinsic asthma”. Prescriptions given for allergic medications.
ICD code – J45.909.
Here we do not code exacerbation as the Physician has not diagnosed as exacerbation.
Asthma ICD 10 Example 2:
45 year old female who works in a textile factory, came to clinic with her daughter. She has wheezing from past 3-4 days. She smokes 3 packets of cigarette daily. Also, she has a history of COPD and asthma.
After examining the patient, physician orders a chest X-ray and given nebulizer treatment at the clinic.
Final Assessment: COPD exacerbation, Asthma exacerbation
Codes – J44.1, J45.901, F17.210
Need to code both asthma and COPD because asthma with additional specificity can be coded along with COPD.
Asthma ICD 10 Example 3:
Martin, 50 year old male visits the clinic for occasional wheezing. He does not use any type of tobacco products. He does remember that he had Asthma during his childhood, but after 10 or 11 years he never got any of those symptoms again.
Physician ordered for chest X-ray and checked peak flow. He concluded in the final assessment as “mild intermittent asthma”. He did not prescribe any medicine, but suggested to visit the clinic when get symptoms next time.
This case leads to ICD J45.20 in the ICD-10- manual.